Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of . — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. access control has two main components: Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access.
from www.techtarget.com
Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. access control has two main components: Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers.
What is RoleBased Access Control (RBAC)? Definition from TechTarget
Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. access control has two main components: Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT MODULE 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1688144 Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Access control is crucial to identity and. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
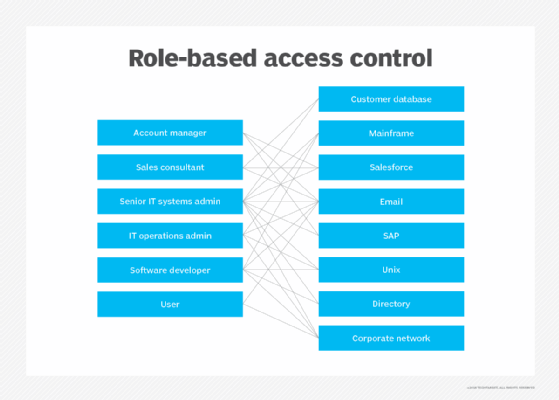
From exotrdzdb.blob.core.windows.net
Example Of Access Control System at Edward Kroll blog Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Authentication Authorization And Access Control Studypool Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. in its simplest form, access control involves. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.oreilly.com
Access Control Process Access Control and Identity Management, 3rd Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of access control has two main components: — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. Authentication. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From peligro-e-portfolio.webflow.io
Module 5 Implementing Access Control, Authentication and Account Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. access control has two main components: Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. in. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Authentication and access control overview PowerPoint Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. explore access control as a vital. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From thecyphere.com
Access Control Security Types Of Access Control Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. access control has two main. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION Authentication Authorization And Access Control Studypool Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. access control has two main components: — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. Authentication. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.f5.com
What Is Access Control? F5 Labs Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.g2.com
Access Control Technology Glossary Definitions G2 Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.xorlogics.com
6 Tips for Implementing Access Control Authentication System With Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. access control has two main components: in its. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.identity.com
Authentication vs. Authorization Key Roles in Access Control Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From interval.com
Authentication and access control Interval Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Robust access controls secure. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) CovidBChain Framework for access‐control, authentication, and Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use cases and ensuring. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.liveenhanced.com
User Authentication and Access Control Crucial Salesforce Security Steps Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. access control has two main components: in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. . Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From slidetodoc.com
Access Control Authentication and Public Key Infrastructure Lesson Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of — access controls authenticate and authorize individuals to access the information they are allowed to see and use. Access control is crucial to identity and access management (iam) strategies, helping organizations navigate modern cybersecurity challenges. Robust access controls secure sensitive data by making it hard for hackers to gain access. — examples of controls for managing physical access. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.studypool.com
SOLUTION 14 authentication and access control Studypool Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of access control has two main components: Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. explore access control as a vital data security measure, protecting digital resources across use. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Passwords, Authentication, and Access controls PowerPoint Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of — examples of controls for managing physical access include gates, locks, keypads, and biometric readers. Authentication verifies a user’s identity, while authorization determines what that verified user can access within a system. in its simplest form, access control involves identifying a user based on their credentials and then authorizing the appropriate level. Robust access controls secure sensitive data. Access Controls Authentication Controls And Integrity Controls Are All Examples Of.